Digestive anomalies could occur in adults as well as in children. Their severity may range between mild pain and those that demand medical attention. The persistence of symptoms or difficulties in their detection can be addressed through medical tests like EGD that provide clues on the causes. Below, you will find the facts regarding the digestive disorders, the EGD role, and the contribution of this procedure to the detection and diagnosis:
What is Digestive Disorders?
Digestive disorders are a series of disorders experienced in the gastrointestinal system, including the esophagus, stomach and intestines. The cause of these disorders could be as a result of many factors including diet, genetic and lifestyles. The typical conditions are acid reflux, ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and Crohn. The symptoms may consist of stomach pain, flatting, nausea, diarrhea, or hard time with swallowing. The complicated structure of the digestive system and similarities of symptoms of different conditions may complicate the identification of their specific origin. Such a complexity requires the use of sophisticated diagnostic instruments in order to investigate and assess the affected areas.
The question What Is EGD comes to mind as well.
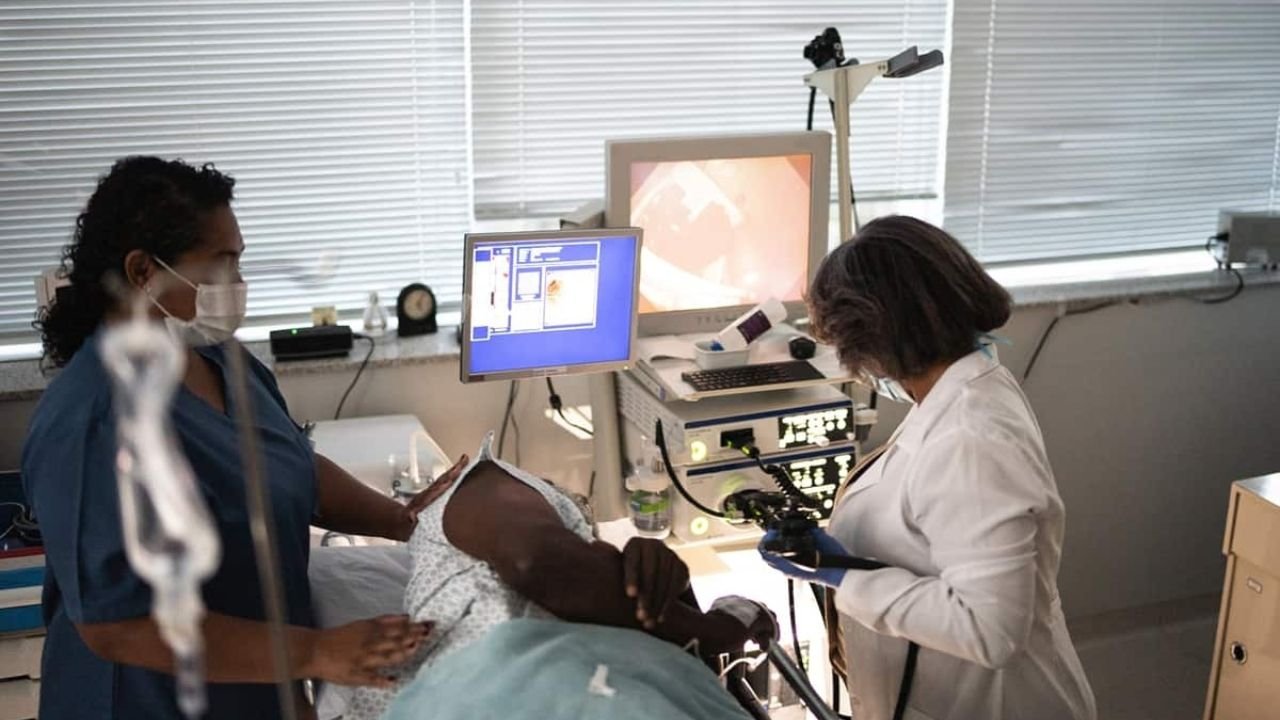
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy in common terms known as EGD comprises a test used to check the upper gastrointestinal tract. The parts in this region involve the esophagus, stomach and the initial member of the small intestine or the duodenum. In the process, a thin pliable tube with a camera at the tip, known as an endoscope, is fed into the mouth and utilised through the throat so as to record images of the upper GI tract in detail.
During EGD, a trained gastroenterologist carries out the procedure and lasts up to 30 minutes. Patients under the treatment process are normally sedated to reduce pain, but the process is considered to be non-invasive. Using this procedure, the GI tract can be visualized directly and the physician is able to detect abnormalities, get muscular tissues in case of requirements via biopsies and minimize treatment during the procedure.
What is the role of EGD in diagnosis of digestive problems?
EGD provides useful information on the diagnosis and identification of several upper gastrointestinal conditions. Unlike the external tissue imaging tests, the process is known to actually look into the lining of the tissue. This aspect enables the doctor to identify deficits that cannot be identified in X-rays or ultrasounds. The characteristic inpatient diagnoses to EGD are:
- Identification of Structural criticism: EGD may identify structural problems like strictures (narrowing of the esophagus), hernias or tumor. This evidence could be the cause of such symptoms as problems swallowing, pain, or chronic reflux.
- Signs of Disease: The endoscope provides a visual diagnosis to see whether the stomach and esophagus is red, swollen or has any erosion which is a symptomatic diagnosis of diseases such as gastritis or esophagitis. EGD also helps identify the symptoms of Barretts esophagus, which is a chronic reflux.
- Identifying and Evaluating Bleeding or rather Ulcers: The patient who presents with the gastrointestinal bleeding will often benefit from EGD because the endoscope is able to show where the bleeding is coming from; this can either be an ulcer, a tear or a lesion. Interventions, including cauterization, can stop the bleeding process by going through the procedure.
- Diagnosis Exclusion or Confirmation: Tissue samples obtained during an EGD may aid in confirming the diagnosing of diseases such as celiac disease, infections or cancer to allow the certainty needed to change or treat accordingly.
- Communication benefits: EGD can help guide treatment strategies by identifying the concrete cause of the symptoms in order to provide a specific treatment program, including and not limited to dietary changes, use of medicine, or additional procedures.
Read More EGD and Diagnostic Advantages
Fiagaing to interpret the contribution of EGD in diagnosing gastrointestinal disorders is one of the steps required to deal with chronic gastrointestinal symptoms. Due to its ability to facilitate real-time visualization and the fact that it can analyze a wide range of conditions, this procedure has become both feasible to the patients and health care professionals. In case you have the feeling that you have a digestive disorder or even feel the need to know whether EGD may be a fitting choice as a diagnostic tool, the best alternative is a visit to a gastroenterology expert who will advise you.