The digital systems are currently producing huge data within seconds. There are sensors, smart devices, machines, and applications that generate information that requires an immediate response. The conventional cloud computing cannot match such demands on time. Thus, companies nowadays use more lines to use Edge Computing on the Sidelines. to work with the data where they are generated and provide quicker results.
Rather than transmitting all the data to remote data centers, edge computing processes data on the local level. Consequently, the organizations decrease delays, enhance reliability, and open up real-time intelligence. This change alters the industries that require speed, precision, and responsiveness.
Table of Contents
Understanding Edge Computing at the Sidelines
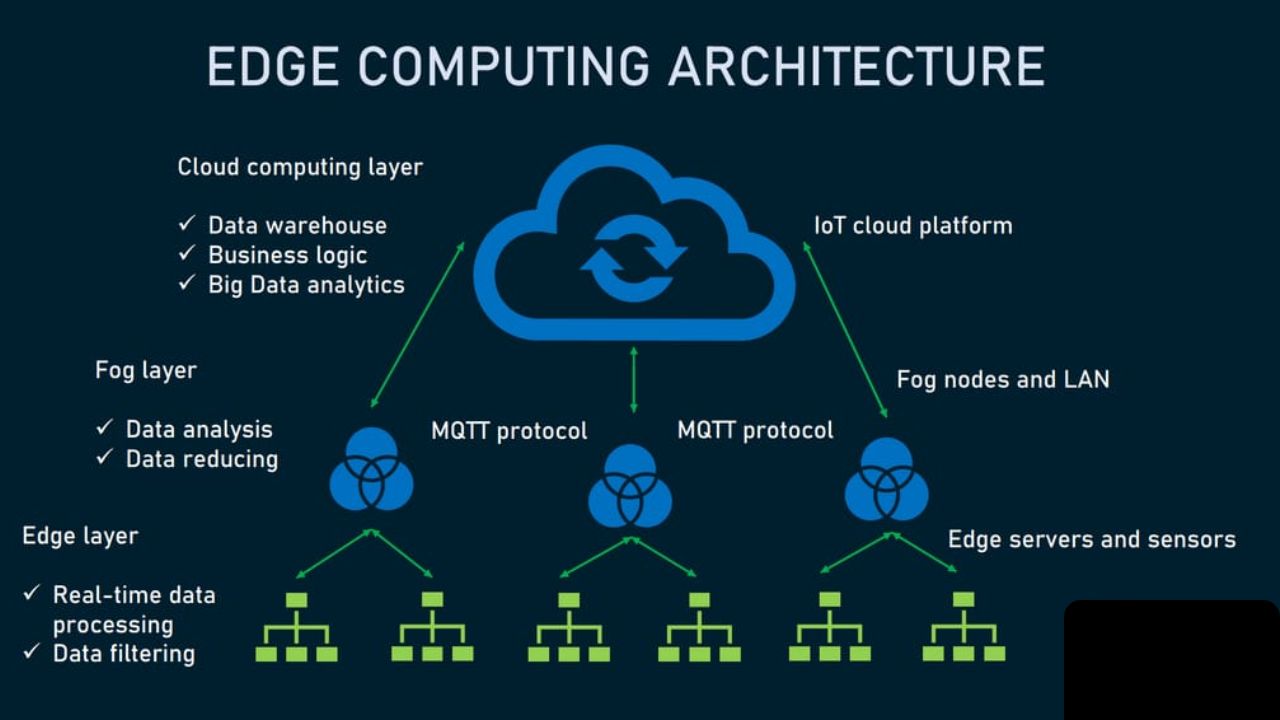
Edge computing computes data, instead of leveraging centralized cloud infrastructure. Sensors, gateways, mobile devices and local servers are some of the devices that process data locally and only send necessary data to the cloud. As a result, systems become responsive and work better.
A factory sensor, a medical monitor, or a smart traffic camera may be an edge device. Such devices process data in real-time and are applicable to use cases that cannot withstand latency. Indicatively, self-driving cars, robotization in the industrial sector, and distance-learning health care all require instantaneous data processing.
In contrast to models that use clouds only, Edge Computing at the Sidelines makes fewer reliance on persistent connectivity. Local systems will still be running even in case network access deteriorates. As such, edge computing enhances its reliability and speed.
Edge Computing at the Sidelines vs Cloud and Fog Computing
Edge computing and cloud computing are used for different purposes. Cloud platform is good when it comes to large scale storage and complicated analytics. They however have difficulties with latency sensitive tasks. Whereas, is very effective in real-time decision making.
Fog computing is in between cloud and edge. It introduces a processing unit between the network edge which offers additional processing capacity. Such a distributed architecture distributes workloads and enhances performance to more advanced analytics.
Nevertheless, Edge Computing at the Sidelines is the quickest in the case of real-time applications. It reduces the bandwidth and makes data available to decision points in time. In the meantime, the cloud is still accommodating long-term storage and massive computing.
Benefits of Edge Computing at the Sidelines
Edge computing brings a number of feasible advantages that directly affect business performance.
- First, it minimizes latency since it operates data on a local level. Systems react immediately as opposed to waiting round trips to remote servers. This leads to the enhancement of user experience.
- Second, it reduces the price of bandwidth. Edges devices do not transmit raw data at all but only important information. Thus, the traffic is better managed on networks.
- Third, it leads to reliability. Local processing can be used to ensure that operations can be continued even in the event of a disconnection. This benefit is very crucial in the industrial, healthcare and transportation conditions.
- Moreover, Edge Computing at the Sidelines provides adherence to data sovereignty rules. Companies retain confidential information in geo fences and yet enjoy the benefits of digital intelligence.
Scalability and Flexibility at the Edge
Edge computing does not scale like the conventional models of the cloud. Businesses roll out edge nodes in areas of necessity and grow in small steps. This leads to them not having to make large infrastructure investments.
Intel’s Edge Computing overview results in flexibility since the edge environments are customized to use cases by organizations. Nevertheless, there are orchestration tools like Kubernetes, which remain at the edge. Hence, distributed environments cannot be managed without planning.
In spite of these difficulties, edge deployments change with demands more quickly than centralized systems.
Security and Privacy Advantages
In digital systems, security is a major issue of concern. Privacy is enhanced as it processes data at the location. There is no longer continuous movement of sensitive information in networks which minimizes exposure.
Distributed environments, however, expose more attack surfaces. The edge devices must be well defended. This is why the organizations should introduce encryption, access control, and constant monitoring.
AI and machine learning also enhance edge security. These technologies identify anomaly within a short time and act on a threat in real time. Consequently, Edge Computing at the Sidelines is a more robust model of security.
Managing IoT Data Efficiently
IoT devices produce large amounts of data. Taking it all to the cloud clogs networks and puts a strain on latency. Edge computing addresses this issue by sorting and processing data on a local level.
As an illustration, industrial sensors identify anomalies in real time and give alerts without delays in clouds. Likewise, patient data are monitored in real-time and assist with quick intervention by healthcare monitors.
When data is processed at the source, organizations can achieve more response speed and have more stable IoT ecosystems.
Challenges Facing Edge Computing at the Sidelines
Even though edge computing has advantages, it has a number of challenges.
| Challenge Area | Explanation |
| Data Sovereignty | Data sovereignty is complex because rules differ across regions. Therefore, companies must ensure compliance with all local regulations. To manage this properly, strong administrative systems are required. |
| Security Risks | Security needs constant attention. Since distributed systems have multiple access points, they create more vulnerabilities for attackers. Organizations must secure devices, networks, and applications at all levels. |
| Scalability Issues | Managing thousands of edge nodes is difficult. As deployments grow, handling updates, monitoring, and maintenance becomes challenging. |
| Workload Management | When edge systems integrate with cloud platforms, workload balancing becomes essential. Proper coordination is needed to ensure smooth performance and reliability. |
| Business Value | Once these challenges are addressed, at the sidelines can unlock significant value for organizations by improving efficiency, speed, and decision-making. |
Opportunities and Innovation at the Edge
The edge computing is introducing innovation in industries.
Data governance requirements in the local markets allow businesses to access new markets. They further enhance the quality of services using real-time analytics.
Dynamic scaling is made possible by microservices and container applications at the edge. Intelligent systems increase the level of automation and decision-making. Therefore, edge computing promotes smarter and faster functions.
The more efficient AI models get, the lighter they become, and the higher the edge deployment capability. Thus, the future at the Side is becoming bright.
Real-World Applications Across Industries
Edge computing is used to predictive maintain and quality control in manufacturing. Sensors identify problems with the equipment in time and save expensive downtime.
Telemedicine and patient monitoring of healthcare is dependent on edge computing. Instant analysis guarantees on-time intervention and improved results.
Autonomous driving and fleet tracking is relied on edge systems in transportation and logistics. Cars analyze sensor information in real time and take precautions.
Edge computing is applied to personalize experiences and maintain inventory in real time by retailers. The optimization of traffic flow, energy usage, and public safety is achieved in smart cities by localized data processing.
These illustrations depict how edge computing transforms sectors with speed and intelligence.
Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing
| Aspect | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
| Data Processing | Local | Centralized |
| Latency | Very Low | Higher |
| Bandwidth Use | Reduced | High |
| Real-Time Use | Excellent | Limited |
| Scalability | Distributed | Centralized |
| Data Sovereignty | Strong | Depends on region |
The Business Case for Edge Computing
Edge computing has direct benefits on customer experience. Quick reaction and real-time customization leads to more satisfaction and loyalty.
- It also enhances faster innovation. Smart automation, edge computing, and AI make businesses develop new digital services.
- Making decisions is now smarter and faster. Organization gets real time information and changes strategies fast.
- Collaboration between ecosystems also increases value provision.
- The major players in the industry promote the hybrid models that combine strengths of the edges and the clouds.
- Gartner predicts that over the near future a majority of the enterprise data would be created and processed outside of a centralized data center.
- Hence, the Edge Computing at the Sidelines is an investment that helps to increase the competitiveness in the long term.
Pushing Infrastructure Toward the Edge
With increased pace of digital transformation, business is no longer limited within a specific scope. Edge locations are transformed to data hubs.
Organizations are successful because of strategic planning. They have to match edge platforms with present and future applications. The choice of vendors is also important, since the risk is minimized through long-term viability.
Analysts are unanimous that edge adoption is motivated by business requirements. Deployment is supported by IT teams, but innovation is usually driven by operational units.
Aerospike and Edge Computing Performance
Aerospike is endorsed edge computing with milliseconds of latency and data processing. Its combined form of memory architecture minimizes the hardware needs and the operating expenses.
Edge protection of sensitive data is provided by security features. In distributed environments, the trust is enhanced by encryption and privacy controls.
Flexibility enables IoT, telecom and retailing applications. Thus, Aerospike helps an organization to scale edge initiatives with confidence.
Conclusion
Edge computing transforms the manner in which organizations process and utilize data. When businesses bring intelligence nearer to the source, they become quicker, more dependable and have control.
Despite these challenges, the problem is resolved with the help of strategic planning and contemporary technologies. Smart automation and real-time insights have already become beneficial in industries.
Digital ecosystems will be growing, and Edge Computing at the Sidelines will continue to drive the continued innovation and define the future of computing.