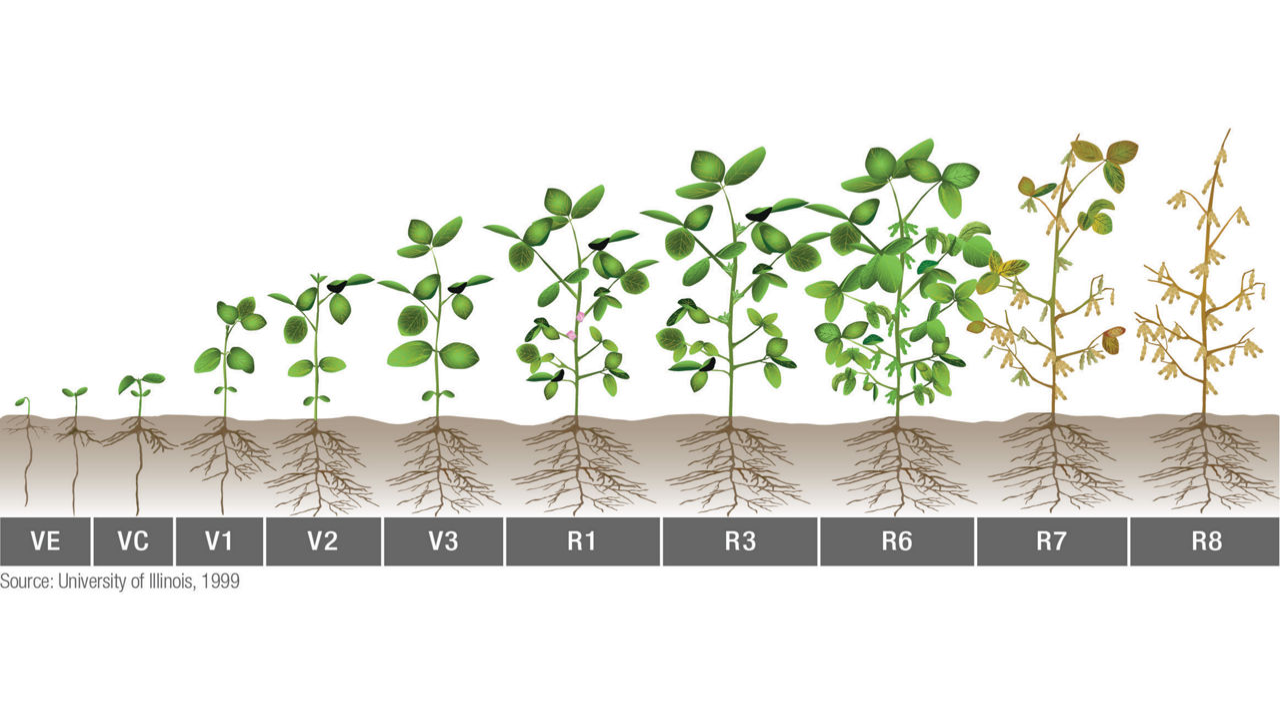
Soybean agriculture expanded across multiple continents after which it became a major crop throughout the United States and Latin America during recent times. The massive increase in popularity stems from rising consumer demand for soybeans and their suitable products for health-friendly diets among vegetarians and vegans. The understanding of their developmental process remains essential for all stakeholders.
Soybean plants need proper pest control measures to develop normally. Residents of Pensacola who need pest control services should look to professional companies to keep their crops pest-free thus achieving higher yields. Any plant protection service provided by professionals ensures natural plant health while supporting long-term agricultural sustainability.
Soybean cultivates without great difficulties in most conditions. When offered appropriate amounts of sunlight together with warmth and moisture the plant succeeds. Despite this soybean remains susceptible to several pests and diseases and experiences the negative effects of waterlogging and early-stage frost. Research institutions including public and private entities join forces with farmers to establish new agricultural technologies as well as best farming practices. Soybean cultivation depends on prompt planting together with thorough monitoring and harvesting at the correct time.
The following passage provides an in-depth explanation of all important facts regarding Soybean growth and development.
Necessary Conditions For Soybean Growth
Certain environmental elements promote the successful growth of soybeans. You need to spot these conditions because exposing your soybeans to such ideal environmental factors will improve their development and productivity. U.S. soybean farmers conduct ongoing research which focuses on enhancing plant varieties alongside better agricultural practices and pest and disease control alongside climate change adaptation strategies.
The climatic environment supports soybeans to flourish best in the tropical and sub-tropical conditions of Indonesia as well as the cold-temperate locations of Canada and the Americas. Soybeans thrive at locations that have adequate water supply of 510 to 660 millimeters per season and intense temperatures between 22 and 35 degrees Celsius.
Different soil profiles are suitable conditions for growing soybeans because they require minimal soil requirements. For achieving maximum soybean yield cultivation must occur in loamy soil with organic matter and proper drainage and pH levels within 6.0 to 7.5 range. The growth environment of legumes becomes toxic because aluminum and manganese become available when the soil pH drops below 4.5. Acidic conditions above pH 8 usually fail to provide the essential micronutrients including zinc and iron which are vital for soybean development.
Steps Involved in Soybean Planting
Multiple simple instructions guide the process of planting soybeans.
Your operations before planting need to happen right after the first step. Among all processes tillage stands as the most essential factor. The process of ground preparation helps seeds can easily establish and germinate their fragile young plants. The seeds require pesticide along with fungicide treatment after the completion of tillage procedures. You should remove pesticides and fungicides before proceeding to plant the seeds.
You should monitor for the right planting season following pre-planting procedures because it generally happens during late winter and early spring. Proper timing of seed planting protects the developing beans from inadequate soil moisture and undesirable weather elements which minimize crop yield and maturity rates.
You should commence the seed planting at the correct moment during late winter or early spring once the seeds reach their appropriate state. Broadcast soybean seeding worked once before yet soil-driven organized seeding delivers better results for reaching high production levels. Proper seed spacing promotes yield increases while the crop develops canopies that help pest management.
The Growth Time & Harvesting
During day 100 the soybean plants enter their terminal growth phase prior to becoming mature. The growing period depends on seasonal variations together with daylight and nighttime durations. The duration of sunlight in longer day cycles delays flowering in short-day cultivars while increasing both plant height and number of nodes in bush growth. A lower number of daylight hours promotes the process of flower development. The variation in maturation periods results from this factor.
Every harvesting operation needs to take place at the precise moment. Too early harvesting results in immature bean production yet delayed collection brings about substantial losses of productivity. Before harvesting soybean seeds you need to examine both maturity status and moisture content in the seeds.
Handling Pests and Diseases
Soybeans demonstrate higher resistance compared to other legume crops yet pests alongside diseases reduce their total production significantly. Environmental conditions together with farming practices and historical disease occurrences control the likelihood of pest and disease attacks of soybeans.
Three prevalent soybean pests consist of grasshoppers together with stink bugs and bean-leaf beetles (BLBs). BLBs represent the most damaging group of pests that affect growing soybean plants throughout their entire development period. During the later stages of soybean growth grasshoppers along with stink bugs attack leaves and pods respectively. Herbal pest control methods offer a solution to reduce pest populations for improved soybean output.
During its life cycle the soybean interacts with hundreds of pathogen types yet only specific pathogens cause severe yield reductions. The major diseases which infect soybean plants are Downy mildew and Bacterial blight and White mold and Stem canker and Charcoal rot. Most of these diseases remain manageable through the combination of non-host crop rotation along with resistant cultivars, seed treatments and deep tillage and fungicides.
Soybean and Biotechnology
Scientists and researchers have extensively worked to develop contemporary techniques which boost soybean yield production for delivering to rising worldwide demand. The research field of bioengineering yielded GMO soybeans as a result. Generically modified soybeans form the majority of American soybean crops which primarily serve as feed for animals while producing soybean oil. The pest-resistant attributes in GMO beans result in increased production levels. The goal of biotechnology in soybean cultivation focuses on achieving greater hectare yields and managing pest control equations.
Bottomline
Soybean belongs to a group of legumes which demonstrates outstanding ease when it comes to cultivation. All required steps significantly impact crop outcomes when combined with correct soil preparation that includes necessary nutrients. Using pre-planting seed treatments allows farmers to minimize pests and diseases while improving seeding and plant development. Proper management and timely harvest of the crops at full maturity produces remarkable improvements. You need to understand modern technology for halting diseases while boost crop growth output.
It is essential to identify correct Pest Control methods together with tracking soybean developmental phases. The early management of pests guards your crops against severe destruction thus producing improved health and production amounts.