Dive headfirst into the captivating universe of chromatography!
Embark on an enlightening journey to unravel the intricate tapestry of Reversed Phase Columns and their pivotal role in achieving unparalleled accuracy in analytical results Now, let the scientist within you break free!
Journeying Through Chromatography Analysis
Trace back the annals of time to 1903, where Russian botanist Mikhail Tsvet introduced chromatography, a revolutionary technique for separating mixtures. From the rudimentary paper chromatography in the 1940s to the sophisticated high-performance liquid and gas chromatography of the 1970s, this method has continuously metamorphosed, enhancing efficiency and expanding its application horizon.
Navigating Chromatography Principles
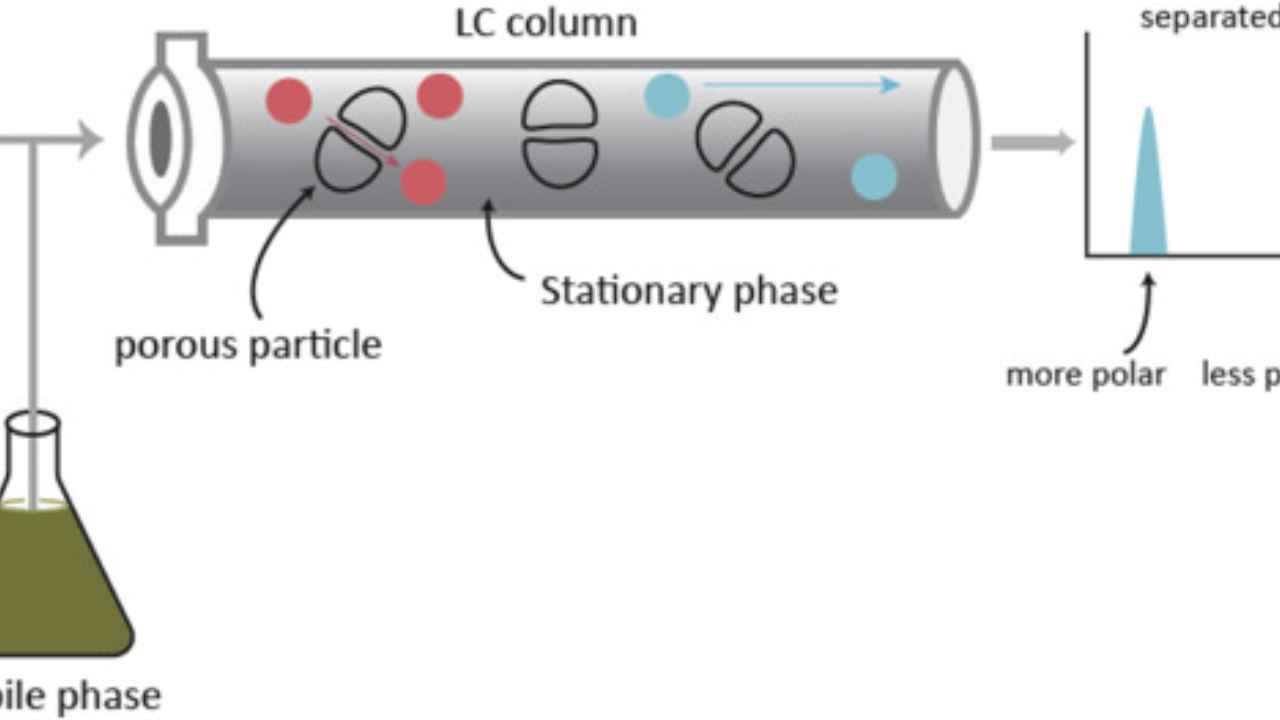
Chromatography, a scientific alchemy, delicately separates mixtures into their elemental components. It orchestrates the dance of a ‘mobile phase’ carrying dissolved mixtures over a ‘stationary phase.’ The components, with varied interactions with these phases, elegantly part ways. This fundamental principle underlies an array of chromatographic procedures, serving as the bedrock of the analytical realm.
Chromatography’s Versatility Across Fields
The significance of chromatography extends its tendrils into diverse fields, notably pharmaceutical and forensic labs. A stalwart separation technique, it identifies and purifies components in mixtures, acting as the linchpin in drug testing, pollutant detection, and substance composition analysis. In the complex tapestry of chemical analyses, chromatography emerges as an indispensable tool.
Demystifying Reversed Phase Columns
Now, let’s delve into the mesmerizing realm of the Reversed Phase Column, a luminary in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). With a hydrophobic stationary phase and a polar mobile phase, it orchestrates the separation of organic compounds based on polarity, casting a spotlight on critical insights for chemical and pharmaceutical research.
Embarking on a Tour of Reversed Phase Column Types
Reversed Phase Columns, the monarchs of liquid chromatography, exhibit diverse types defined by their bonding phases. C8 and C18 columns, with their carbon chains, wield varying hydrophobicity. Phenyl and cyano columns, with unique selectivity, add layers to the chromatographer’s palette. Pore size, particle size, and column length further paint the canvas, influencing separation efficiency and resolution.
Unveiling the Choreography of Reversed Phase Chromatography
Behold Reversed Phase Chromatography (RPC), a liquid chromatography ballet that capitalizes on hydrophobic interactions to segregate compounds. Non-polar compounds, drawn to the hydrophobic stationary phase, pirouette gracefully, eluting slowly. This technique’s prowess shines when dissecting complex mixtures of non-polar or moderately polar compounds, revealing its paramount importance.
The Enchanting World of Books
Books, with their magical allure, beckon us into realms of countless worlds, characters, and adventures. Beyond portals of knowledge, they fuel curiosity, nurture imagination, and broaden perspectives. These literary enchantments, limitless in their impact, encapsulate the boundless wonders nestled between their pages.
Reversed Phase Column’s Symphony in Chromatographic Analysis
In the orchestration of chromatographic analysis, the reversed phase column stands as a linchpin, acknowledged for its prowess in separating mixtures. Its predictability and reproducibility set the stage for consistent results, enabling analysis of a broad spectrum of polar and non-polar compounds. Versatility and precision intertwine, defining the backbone of chromatographic accuracy.
Reversed Phase Columns: Pioneers Across Chromatographic Techniques
Reversed Phase Columns ascend to prominence across various chromatographic techniques, notably in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Their non-polar stationary phase emerges as a virtuoso, facilitating exceptional separation of substances, especially organic compounds. The hydrophobic tango between sample and stationary phase cements the indispensability of reversed phase columns in chromatographic analysis.
The Dynamics of Reversed Phase Columns on Analysis Accuracy
Reversed phase columns elevate the accuracy of liquid chromatography analysis to unprecedented heights. Through the hydrophobic dance on a stationary phase, these columns masterfully separate complex mixtures and analytes. The result: heightened specificity, reproducibility, and accuracy in measurements, fundamentally shaping the precision of the ensuing analysis.
Weighing Pros and Cons of Reversed Phase Columns
In the dichotomy of chromatography tools, reversed phase columns unfurl both pros and cons. High resolution, reproducibility, and solvent flexibility emerge as merits. Yet, pitfalls lurk in unwanted secondary interactions, limited pH range, and the demand for meticulous column maintenance to thwart contamination or degradation.
Navigational Tips for Chromatographic Accuracy
The maintenance and cleaning ballet of a reversed phase column takes center stage, a pivotal act for its optimal functionality. Routine washing with appropriate solvents removes accumulated residues, while vigilant pressure monitoring detects potential clogs. Neglecting this choreography jeopardizes accuracy, reproducibility, and the lifespan of the equipment.
Creating the Optimal Chromatography Ambience
Within the chromatography arena, an optimal environment and conditions are paramount for accuracy. Controlled temperature, minimal dust, and vibration, coupled with a chemical-contaminant-free space, form the backdrop. Frequent calibration and proper equipment maintenance are prerequisites, as are high-quality solvents and samples, essential for reliable results.
Harmonizing the Chromatography Technique Selection
The selection of the right chromatography technique becomes a harmonious symphony in separation science. Factors such as sample nature, required resolution, sensitivity, speed, and cost compose the score. Gas chromatography, liquid chromatography, or ion chromatography emerge as tailored techniques, each contributing to specific testing needs.
Technological Crescendos in Reversed Phase Columns
Technological crescendos resound in the evolution of reversed phase columns for chromatography. Innovations echo in enhanced stability, improved separation efficiency, and heightened reproducibility. The result: swifter analyses and finer particle sizes, underscoring technology’s pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and precision of reversed phase column chromatography.
Reversed Phase Columns: Trailblazers in Futuristic Chromatography
As we gaze into the future, reversed phase columns emerge as trailblazers, propelling chromatography into new dimensions. Elevating separation efficiency, accommodating a broader range of compound analysis, and boasting advanced chemical stability, they become beacons in modern bioanalysis and pharmaceutical fields. Their significance manifests in precision, efficiency, and speed when processing complex samples.
Reversed Phase Column FAQs: Navigating the Enigma
Navigate the enigma of reversed phase columns with key insights. C18 columns unravel their reverse-phase nature, excelling in the separation of organic compounds. Their usage in HPLC stems from superior retention and separation capabilities. The significance of reversing an HPLC column lies in back-flushing, an essential cleaning chore for sustained peak performance.
In this kaleidoscopic journey through chromatography and reversed phase columns, where precision meets versatility and reliability intertwines with innovation, embrace the scientist within and redefine your analytical experience.”