Childbirth exists as a meaningful reason for joy. Birth often differs from expectations since it causes injuries to newborn infants for some families.
Birth injuries include both light traumatic situations together with severe and permanent harm. Natural birth complications along with delivery mistakes both work as contributing elements toward these injuries of newborns.
By knowing the factors that lead to preventable injuries during childbirth parties need to understand the mechanisms that cause such harm. The following section examines the leading eight components that cause birth-related injuries in infants. Such knowledge enables parents to recognize significant indicators which they should watch during both their pregnancy and delivery process.
1) Oxygen Deprivation:
The brain together with the entire body of a newborn requires uninterrupted access to oxygen. The disruption of oxygen supply or its deprivation results in rapid development of dangerous healthcare issues. Asphyxia functions as a primary factor leading to oxygen deprivation when patients cannot breathe normally to receive sufficient oxygen supply to the body. The neck compression of the baby during umbilical cord wrapping blocks their oxygen supply. Placental abruption functions as a factor that causes placenta to separate from the uterine wall preventing proper oxygen transfer.
Umbilical cord prolapse together with unstable blood pressure and respiratory problems or delayed urgent C-sections forms additional risks for asphyxiation. The prolonged absence of oxygen leads to serious brain damage as well as organ failure alongside permanent disabilities in babies. The family of a birthing patient may decide to review legal options when injuries arise because of substandard fetal distress monitoring or response. The need for cerebral palsy lawsuit consultation would arise in cases where cerebral palsy develops from medical professional negligence.
2) Trauma During Delivery:
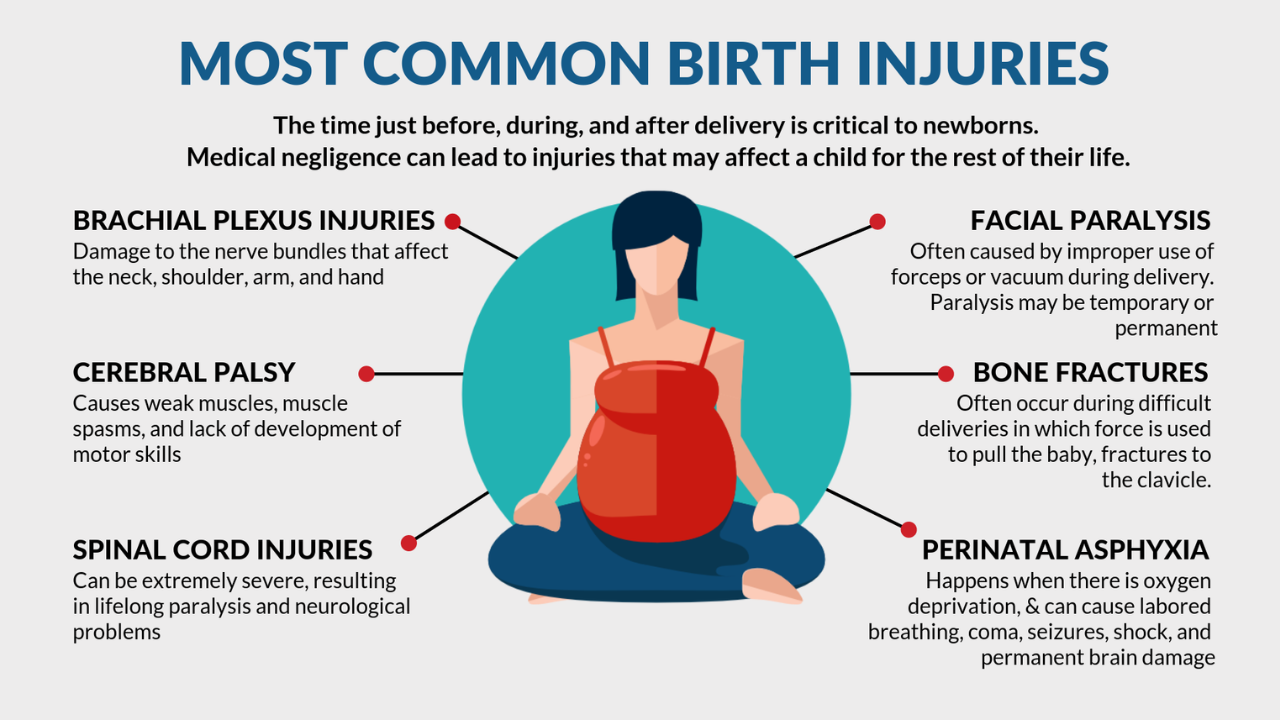
Pressure applied to the mother during childbirth may lead to injuries that affect her baby. The improper usage of forceps or vacuum tools represents potential causes of newborn trauma during delivery. The delivery tools that doctors use to assist delivery pose risks of head injuries if medical teams position them incorrectly. Inadequate placement can lead to skull traumas such as cuts and bruises or skull fractures. Incorrect head positioning during delivery procedures leads to damage of neck and spinal cord nerves.
Beside the mother the birth canal travel difficulty exposes newborns to potential risks. Any combination of slow delivery together with irregular fetal position coupled with a large birth size can severely harm the newborn child. Errors in episiotomy procedures can also occur among medical professionals. Statements need precision when performing perineal cutting since improper accuracy may result in harm to the baby. A wrong application of forceful traction by the obstetrician or improper episiotomy incision can result in shoulder dislocation or facial damage in the newborn.
3) Premature Delivery:
Medical complications along with injuries become more dangerous for newborns delivered earlier than 3 weeks. A premature infant experiences organ and body system immaturity which leads to unpreparedness outside the womb. The absence of surfactant in premature lungs generates respiratory distress syndrome. Infections of severe danger threaten premature babies because their weakened immune system cannot protect them.
Preterms often experience both low birth weight along with neurological complications that result in intraventricular hemorrhage. Medical stabilizations conducted on premature babies with extremely-low birth weight frequently produce some injuries during the critical care phase. Medication errors together with breathing support mistakes and delicate tissue handling mistakes also result in injuries to premature infants. The care of premature infants demands continuous monitoring because failure in monitoring could result in preventable medical errors so prevent further damage from occurring.
4) Prescription Drug Exposure:
The developing baby becomes affected by specific medications which pass through the placenta which doctors provide to pregnant women. The use of drugs during pregnancy leads to birth defects together with low birth weight followed by withdrawal symptoms that cause behavioral issues in newborns. The use of opioid painkillers leads to the development of neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) which causes newborns to experience withdrawal symptoms due to drug exposure during pregnancy.
Medical injuries emerge due to doctors providing insufficient risk disclosure to pregnant women or through their failure to prescribe medications with required caution. Three factors that cause harm to infants are poorly controlled chronic medical conditions together with improper drug dosage administration as well as insufficient monitoring for drug effects after birth. The implementation of pre-birth prescription drug detection systems would prevent numerous birth defects from happening to infants.
5) Undiagnosed Birth Defects:
Medical conditions present during pregnancy before birth may lead to injuries since birth defects remain impossible to prevent. Healthcare providers detect these conditions because it enables them to organizes specialized delivery procedures which prevent traumatic outcomes. Medical staff alongside parents face challenges in identifying birth defects through prenatal screening which results in unsuccessful detection of these conditions for all parties involved.
Slab defects connected to brain or spinal malformations raise newborns at risk for labor-induced nerve damage. A lack of diagnosis in growing issues may generate injury to the muscles and skeleton structures because of small dimensions. The absence of preoperative high-risk condition detection hinders medical professionals from implementing complete dangerous delivery prevention strategies for newborns.
6) Poor Communication Between Providers:
Multiple healthcare providers who assist with childbirth include obstetricians as well as pediatricians and anesthesiologists and nurses. Newborn injuries occur when caregivers within the treatment team fail to properly communicate with one another. The lack of appropriate communication among medical specialists results in inaccessible vital information among healthcare professionals.
A doctor will not detect fetal distress if the hand-off of heart rate monitoring is insufficient. The pediatrician might unexpectedly receive little information about post-delivery treatments which specific complications require. Each handover between practitioners in labor creates an opportunity for fundamental clinical errors and crucial mistakes which occur due to communication lapses.
7) Inadequate Emergency Response:
The health of a baby remains at risk because unforeseen delivery emergencies tend to arise without warning. Acting quickly becomes essential when the umbilical cord prolapses or placental abruption occurs because both conditions threaten life-threatening emergencies. The response of medical teams that demonstrates poor quality along with inadequate intervention protocols leads to preventable infant injuries. Delaying emergency C-section procedures occurs when medical staff fail to identify labor-related fetal distress indicators properly.
The coordination breakdown between healthcare units that handle mother and baby transfers result in poor standard of care. Insufficient resources as well as lacks in medical staff during emergency scenarios both result in harm to infants. The avoidance of negligent emergency actions requires well-established protocols alongside proper preparations since every second counts in these situations.
8) Failure to Prevent Infections:
Newborn infants possess inadequate immunity that exposes them to risky birth-related infections throughout the delivery period and beyond birth. Medical staff must perform proper hygiene procedures alongside infection prevention measures to stop bacterial and viral transmission attacks on newborn infants. The improper implementation of procedures allows harmful pathogens to reach babies.
Inadequate hand washing along with improper sterilization of delivery room instruments leads to fast infections between healthcare providers. The lack of detection of maternal infections during pregnancy results in transmission between mother and baby. Medical facility infections like MRSA obtained during nursery care generate severe problems such as sepsis together with meningitis along with other serious complications. Public health viruses as well as other standard bacteria develop into dangerous infections in newborns when improper disease isolation methods are practiced.
Current infection prevention methods combine maternal evaluation with pathogen tracking as well as separating infected newborns and requiring strict cleanroom practices in all patient areas. Facilities that fail to practice infection control are determined guilty of medical malpractice. Death or serious illnesses and brain damage may trigger the possibility of malpractice investigation which leads to lawsuits. The prevention of infections protects the fundamental security of susceptible newborns.
Conclusion:
Childbirth must remain free from physical harm and lasting disabilities to pregnant women. Some complications of birth occur naturally but medical professionals can stop many avoidable birth incidents through correct treatments. Safe birthing practices under guidance from education and changes and careful protocols will safeguard babies from avoidable injuries during and after birth.